How to Improve Brain Function and Increase Your Healthspan After 50
How to Improve Brain Function and Increase Your Healthspan After 50
The aging process can be overwhelming for many of us, and it’s normal to feel a little down when we think about all the changes that come with it. However, it’s important to retain perspective and keep in mind that aging is a natural part of life and not something to feel sad about.
In recent years, remarkable advances in age-related technologies have made it possible to improve physical, cognitive, and emotional well-being as we age. The number of older adults in the world population is expected to double to 1.6 billion within 30 years, according to a report by the World Economic Forum. But although life expectancy has increased substantially since the 1960s, a report by McKinsey Health Institute notes that many people will spend those extra years in a state of relatively poor health.
Thankfully, advancements in medicine are helping to redefine both lifespan and healthspan.
Healthspan is the number of years that we live an active, healthy, illness-free life. This is the thing that most of us are concerned with as we strive to live our lives fully and with as few health issues as possible.
Remember, aging is a natural part of life, but by adopting positive habits and healthy daily routines, we can all enjoy a high quality of life, even as we enter those senior years. Taking care of ourselves, sleeping right, eating a balanced diet, and exercising regularly are all key when it comes to enhancing healthspan and delaying cognitive decline.
8 Simple Ways to Improve Brain Function and Boost Healthspan
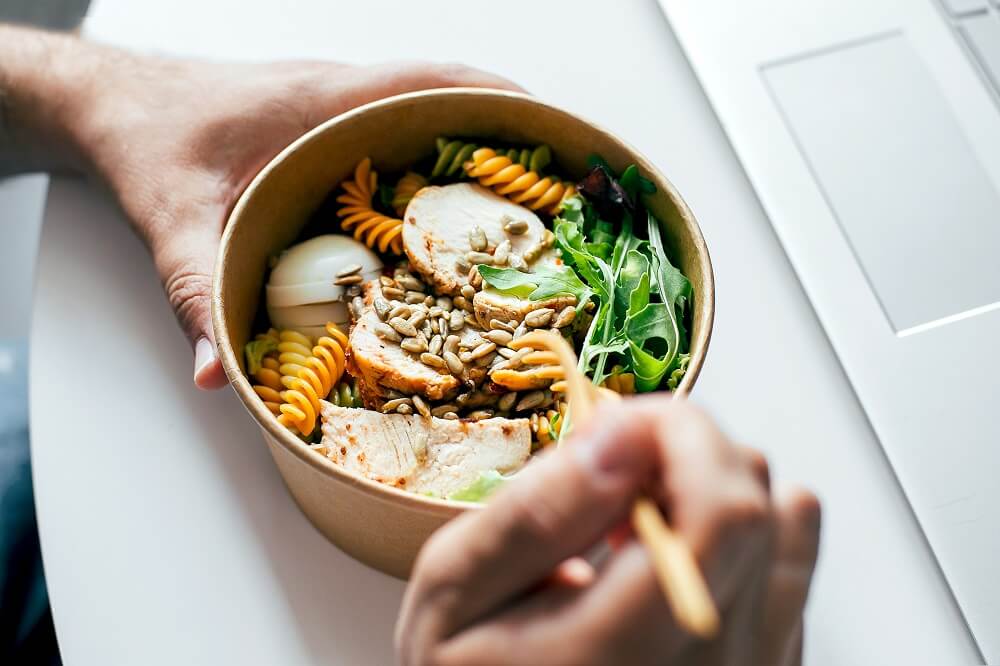
1. Eat For Brain Health and Longevity
Making smart food choices by incorporating a variety of nutritious foods is foundational to healthy aging. A diet high in fiber and low in saturated fat that incorporates fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and fish will help provide the nutrition needed to lower the risk of developing age-related chronic diseases such as diabetes, high blood pressure and heart disease.
To get enough protein throughout the day and maintain muscle, the National Institute on Aging (NIA) recommends adding the following ingredients to meals:
- Seafood
- Dairy
- Fortified soy products
- Beans
- Peas and lentils.
The NIA also advises seniors to drink plenty of water throughout the day to help stay hydrated and aid in the digestion of food and absorption of nutrients.

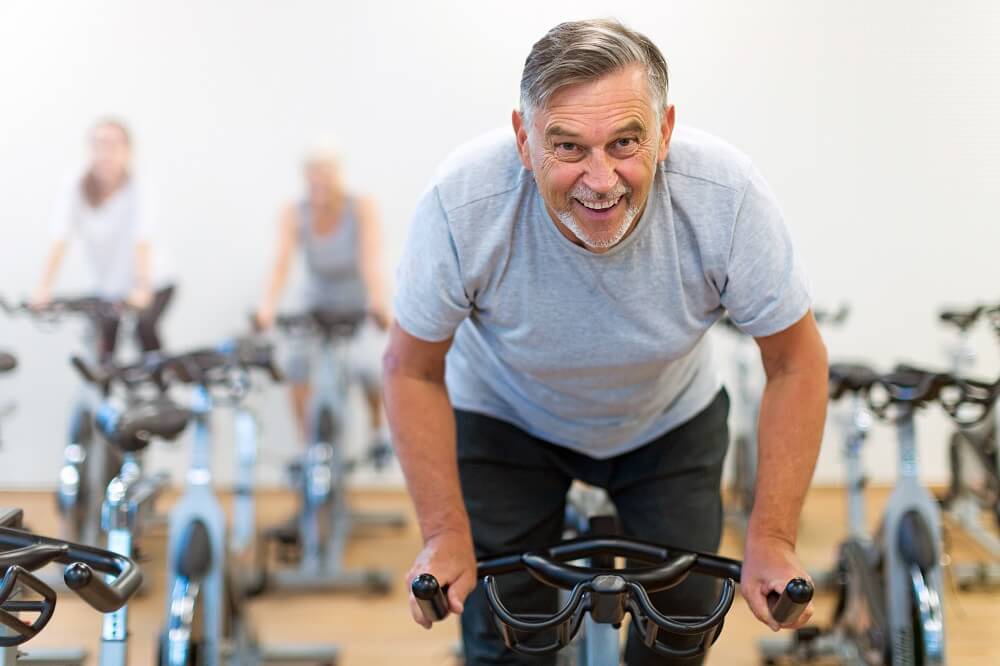
2. Exercise Regularly to Improve Brain Function
Physical activity is important for keeping muscles, bones, and joints healthy and increasing flexibility.
As we age, we lose muscle mass. According to the NIA’s Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging (BLSA), muscle mass and strength typically increase steadily from birth and reach their peak at around 30 to 35 years of age. The BLSA found that after that, “muscle power and performance decline slowly and linearly at first, and then faster after age 65 for women and 70 for men.”
Regular exercise can help older adults increase muscle strength, maintain a healthy weight, and improve mobility and balance, which can help avoid chronic health problems and reduce the risk of falls. The CDC notes that a variety of exercises are best for older adults. Exercise guidelines for seniors include:
- 150 minutes a week of moderate intensity activity such as brisk walking, or 75 minutes a week of vigorous-intensity activity such as hiking, jogging, or running
- Strengthen muscles at least two days a week, working all major muscle groups (legs, hips, back, abdomen, chest, shoulders, and arms)
- Try low-impact options like water aerobics, resistance band exercises, or body weight workouts
- Maintain flexibility and balance with stretching or yoga

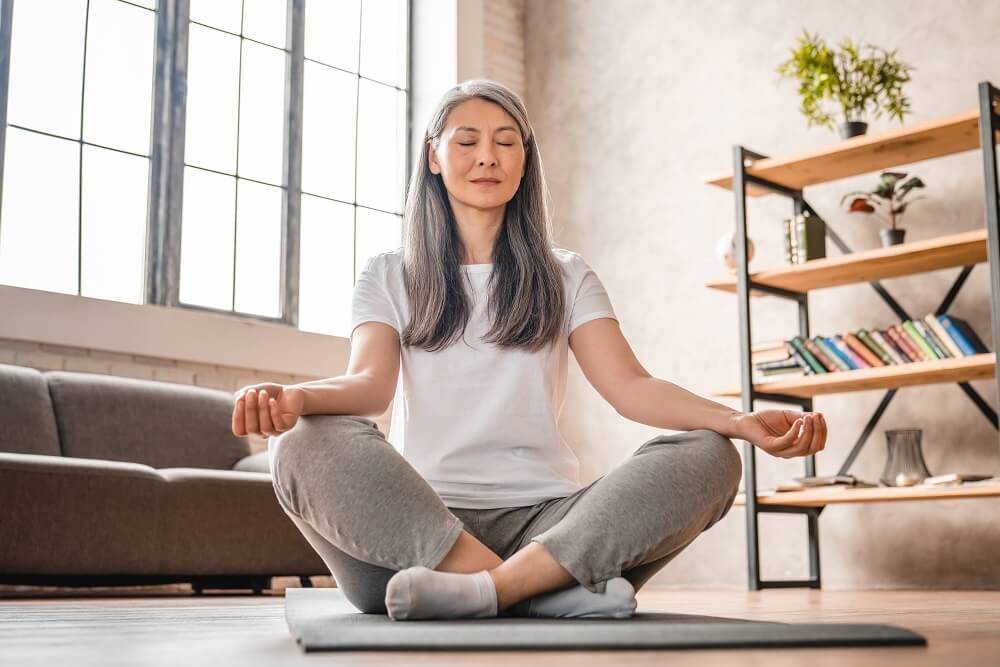
3. Reduce Stress to Protect Cognitive Function
Managing your stress levels is also critical to healthy aging. That’s because high levels of stress release hormones like cortisol, which can increase the risk of anxiety, depression, heart disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, and stroke, as well as induce sleep problems and memory and concentration impairment.
Adopting stress-reducing habits can mitigate stress and promote healthy relaxation:
- Practice mindfulness meditation
- Try yoga or tai chi for focused movement
- Read, listen to music, or pursue hobbies that promote relaxation
- Consider professional counseling for persistent stress, anxiety, or depression

4. Get Good Sleep to Support Brain Performance
Good sleep is vital for helping adults live longer and stay healthy. Some of the impacts of poor sleep include a decrease in attention and concentration and lack of energy. Research also found that poor sleep is associated with greater Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers in cognitively healthy adults at risk for the disease.
The National Sleep Foundation recommends that people 65 years and older get seven to eight hours of sleep each night. Additional tips to sleep better for brain and body health include:
- Avoiding large meals and caffeine before bed
- Maintaining a consistent bedtime and wake-up schedule
- Keeping the bedroom dark, quiet, and cool
- Establishing a relaxing pre-sleep routine
- Avoiding screens (Computer, tablet, phone) for the last hour you’re awake.
Getting sufficient sleep helps the brain and body recover from the day’s exertions and reduces the risk of developing disorders and diseases such as obesity, dementia, heart disease, and stroke.
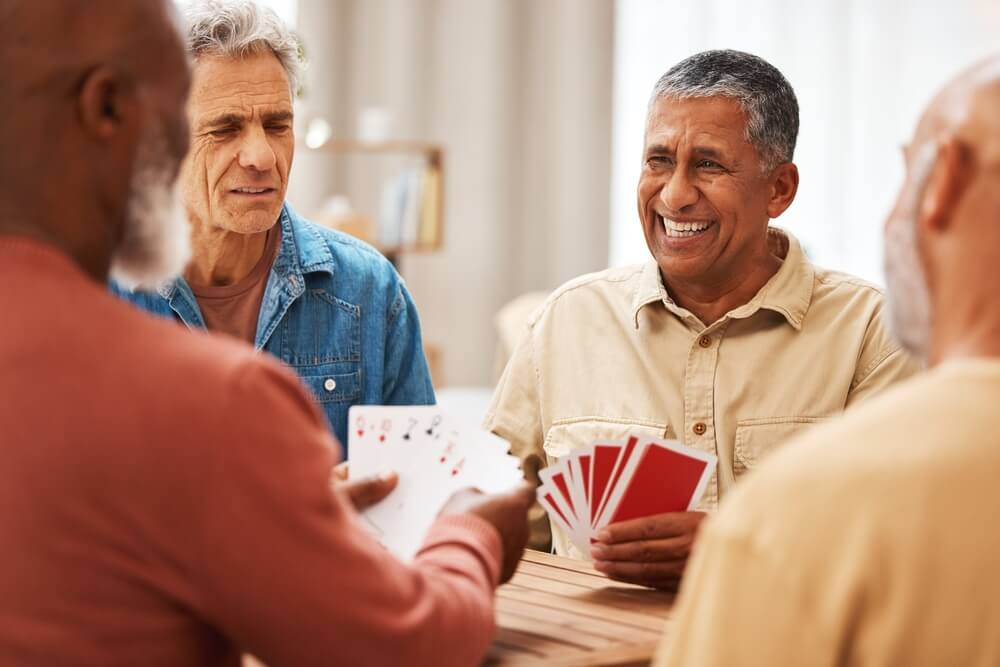
5. Stay Socially Active to Maintain Brain Health
Social interaction has been proven time and again to have a significant influence on physical and cognitive health, particularly in older adults. Numerous studies have shown that being socially active improves and, in some cases, even reverses physical and cognitive decline. Having a good social life means keeping the brain sharp and active, also aiding in concentration, focus, and memory recall.
Social interaction is physically influential as it reduces stress, alleviates loneliness, and promotes healthy habits that are good for the future, especially in healthy agers. However, social interaction is much more than keeping good habits and meeting friends. Having the right social schedule often leads to more regular exercise, support for medical appointments, and more.
Cognitively speaking, active social lives offer much-needed mental stimulation, which can, in many cases, result in new neural connections being built. Regular conversations about various topics are vital to keeping the aging mind sharp and performing optimally. Healthy social interaction is also vital to prevent or reverse depression and anxiety. People who are lonely and perhaps don’t have enough family support benefit greatly from meeting friends regularly, helping to keep their bodies and minds in check.

6. Challenge Your Brain to Improve Cognitive Function
Just as physical exercise is important as we age, so too is keeping the mind active. In fact, a study funded by the National Institutes of Health found that the benefits of cognitive training for older adults can last as long as 10 years. The training, aimed at boosting older adults’ skills in memory, reasoning and speed of processing, slowed their cognitive decline and helped study participants maintain functioning in daily living tasks for over a decade.
Many activities can help keep the mind sharp. To boost cognitive function with brain exercises,
- Play games like chess, sudoku, and crosswords
- Read books or articles that challenge you intellectually
- Try memory exercises or apps designed for cognitive training
- Engage in creative hobbies, such as writing, painting, or music.
Include a mix of activities to stimulate different cognitive functions.
Have you noticed changes in your memory, attention or thinking skills?
Download our free e-book, “What’s Happening to My Brain?” to learn how you can improve your brain health and cognitive vitality at any age.
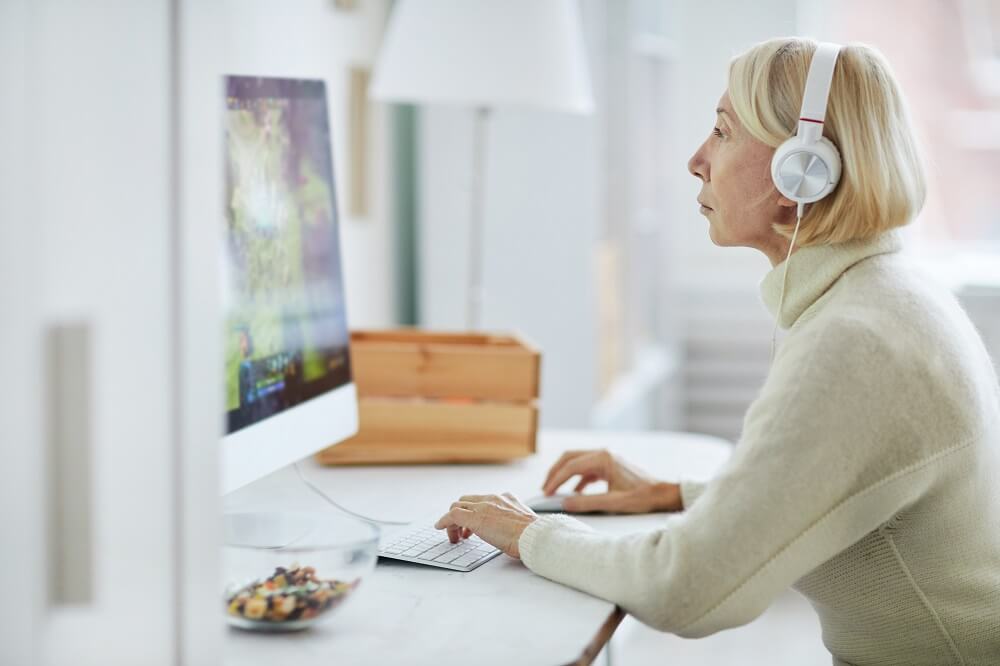

7. Use Technology to Stay Connected and Sharp
Technological advances are transforming the way people age, and can help prevent or even delay cognitive and physical decline. Such innovations are helping aging communities to stay connected and enjoy life fully, even in their golden years.
Technological innovations have the potential to transform the aging process and enhance the quality of life significantly. Consider enhancing your aging and health with:
- Telemedicine for easier access to health care services
- Apps or wearable devices that track exercise or health to track your progress
- Remote monitoring devices for managing chronic conditions
- Social media or video calling to stay connected with family and friends.
8. Explore Innovative Programs to Improve Brain Function
For years, there has been a misconception that declining mental and physical performance is a normal part of the aging process. Aviv Clinics’ personalized medical program is changing that outdated notion.
A new approach to reversing the aging process, the Aviv Medical Program with hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) at its core, treats aging as a disease to help people live healthier, happier, and more productive lives for more years.
Aviv’s medical program is an immersive and highly individualized program that can combine therapies like HBOT, cognitive exercises, physical training, and nutritional and lifestyle coaching to leverage the body’s regenerative abilities. Each comprehensive treatment plan is customized to our clients’ health conditions and improvement goals.
As we age, our bodies become less efficient at channeling oxygen to generate the necessary energy to recover from injury and illness. Boosting the body’s oxygen concentration levels helps improve performance, memory, attention, focus, and other brain-related executive functions, as well as regenerating body tissue, helping healthy aging adults live their best life at any age.
Comedian George Burns once said, “You can’t help getting older, but you don’t have to get old.” Advances in medical science, including hyperbaric medicine, have made that statement truer than ever. At Aviv, we treat aging as a reversible condition, not an inevitability.
Improve Your Brain Function with a Personalized Aviv Program
Ready to take control of how you age?
Contact us today to speak with a client ambassador. You’ll learn how our healthy aging program can help you stay sharp, independent, and active for years to come.
Healthy Aging with Aviv Clinics: watch Dr. Mo on Bloom TV:
Frequently Asked Questions:
What are the best ways to improve brain function as you age?
There are several lifestyle changes you can implement to improve brain function and support long-term cognitive performance, including:
- Consuming a diet high in fiber and low in saturated fat
- Commit to both aerobic and strength exercises
- Adopting stress-reducing habits
- Maintaining a good sleep schedule
- Staying socially active
- Challenging your brain
- Staying abreast of new technology
- Exploring innovative medical programs like the Aviv Medical Program
Can hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) improve cognitive performance?
Yes, clinical evidence reveals that a specific HBOT protocol, when administered in a medically supervised program, can enhance oxygen delivery to the brain and support cognitive function, making it a promising tool for adults seeking to improve brain function and healthy aging outcomes.
Can mental exercises really boost brain function?
Yes. Brain games, puzzles, memory exercises, and learning new skills can strengthen neural connections, improve processing speed, and help maintain cognitive function as you age.
What is the difference between lifespan and healthspan?
Lifespan is the total number of years a person lives, while healthspan refers to the years spent living actively, independently, and free from serious illness. Focusing on healthspan emphasizes quality of life, helping people age with vitality rather than just adding years.
Last Update: September 29, 2025
Early Signs of Cognitive Decline You Shouldn’t Ignore
The term “cognitive decline” encompasses a wide spectrum of neurological statuses. On one end of the spectrum, we find mild cognitive impairment (MCI), a condition that can become more commonplace as we age. Individuals living with this early stage of memory or cognitive ability loss may experience an increased risk of developing a more severe condition. These conditions, including many forms of dementia, lie on the other end of the spectrum. But what are the signs of cognitive decline, and when should you become concerned?
Signs of Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI)
Symptoms of MCI often include:
- Increased forgetfulness. You may take longer to recall someone’s name, miss an important date such as a close friend’s birthday, or blank on a scheduled appointment.
- Interrupted train of thought. This often occurs during conversations or when engaging with entertainment (movies, television, books). You may find yourself rereading the same paragraph two, three, or more times.
- Decision-making stress. Becoming overwhelmed at the thought of making a decision, whether major or insignificant in nature, can be an indication of MCI.
- Confusion in the day-to-day. Many people with MCI start to feel uncertain about “next steps” or understanding instructions.
- Trouble navigating familiar environments. Getting lost on a familiar or frequently traveled route might indicate MCI is present.
- Impulsivity. Acting without thinking things through or expressing poor judgment in certain situations may also be a sign of MCI
- Mental health challenges. Individuals with MCI may present with depression, anxiety, apathy, irritability, or aggression.
Mild cognitive impairment isn’t uncommon and isn’t necessarily a sign of worsening capabilities to come. In fact, some medications and health conditions can cause these same symptoms on a temporary basis.
Most of us notice a gradual slowdown in our mental processes over the years, just as we do in our physical abilities. Although these changes in mental acuity aren’t inevitable, they also shouldn’t be cause for significant alarm — unless they begin to impair our ability to function on a day-to-day basis.
What Is Subjective Cognitive Decline?
A person’s family members or friends might be the first to pick up on symptoms of cognitive decline, but in many cases, individuals themselves recognize something isn’t quite right with their cognitive capacity. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) defines subjective cognitive decline as self-reported confusion or memory issues that have been occurring more frequently or getting worse over the span of a year.
The CDC also notes:
- Overall, the prevalence of subjective cognitive decline (SCD) is 11.1% among Americans (1 in 9 individuals).
- Prevalence is lower among individuals with more years of formal education.
- Nearly 30% of adults with SCD live alone.
- More than two-thirds (66.2%) of adults with SCD have two or more chronic diseases.
- 6% of adults with SCD experienced functional difficulties while performing day-to-day activities or chores.
Given this data, the CDC states SCD is a “growing public health issue.”
When Cognitive Decline Becomes More Severe

While MCI may stabilize or even improve with intervention, symptoms of MCI could also be the beginning of more severe cognitive decline. Many signs of worsening cognitive decline mimic those of MCI, just at more intense levels.
- Confusion becomes much more pronounced. Some people begin to lose track of time or are unsure what day/date it is.
- Making decisions becomes even more difficult, which can lead to frustration and anger towards others.
- Memory loss deepens, with many more instances of forgetting names, dates, places, and events.
- Individuals may be found wandering for unknown reasons, or placing items in odd locations (e.g. car keys in the freezer).
- People tend to have trouble conversing, possibly due to diminished concentration and train of thought.
These factors may contribute to increased social withdrawal. Many people with cognitive decline or dementia understand they’re developing characteristics they may be embarrassed about, or that others find undesirable, and withdraw from friends and family as a result. In other instances, depression or anxiety may prevent them from interacting with others like they used to.
Have you noticed changes in your memory, attention or thinking skills?
Download our free e-book, “What’s Happening to My Brain?” to learn how you can improve your brain health and cognitive vitality at any age.
Unfortunately, social isolation leads to an entirely new set of concerns. Isolated individuals are more at risk for poor health outcomes, self-neglect, and fall-related injuries.
Surprising or Unusual Signs of Cognitive Decline
When thinking about cognitive decline and dementia, people are often aware of the above symptoms (memory, confusion, etc.). But some lesser-known signs of cognitive decline include:
- Changes in sense of smell. A study published in the journal Neurology found that people who could no longer distinguish between two very different odors (e.g. lemons and gasoline) may be in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease.
- Trouble with the law. Dementia sometimes impacts the areas of the brain that control judgment, self-control, violence, and sexual behavior. Individuals with cognitive decline may find themselves in criminal situations, such as theft, trespassing, or even assault.
- Altered sleep patterns. Many people with dementia develop sleep issues such as insomnia, hypersomnia (sleeping too much), or sleeping during the day. This may be due to changes in the body’s circadian rhythm.
- Changes in walking. Slower walking or changes in stride length/gait might indicate dementia-related shifts in the brain.
Take Charge of Your Brain Health With The Aviv Medical Program

Noticing early signs of cognitive decline can be unsettling, whether it’s forgetfulness, slower processing, or difficulty multitasking. At Aviv Clinics, we help clients take proactive control of their brain health with a program built on nearly two decades of peer-reviewed, published scientific research.
For people concerned about declining cognitive abilities, the Aviv Medical Program can include advanced cognitive testing to identify subtle impairments and track meaningful improvements over time. Using evidence-based interventions like hyperbaric oxygen therapy and cognitive training exercises, our program targets the main cognitive domains most often affected by aging, including:
- Memory
- Attention
- Speed of information processing
- Multitasking
- Executive skills
Our board-certified physicians prescribe a personalized treatment program for each client to target their specific concerns and definicencies.
If you or someone you love is experiencing changes in memory or thinking, don’t wait for symptoms to worsen. Contact us to get clarity and start mapping your path forward with Aviv Clinics.
Last Update: July 17, 2025.
Long-Term Effects of Concussion and TBI: How Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy May Help
Traumatic brain injuries (TBI) are much more common than many people realize. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), an estimated 1.7 million Americans sustain a TBI each year. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that there were over 64,000 TBI-related deaths in 2020, which equates to more than 175 brain injury-related deaths every day.
Adults over the age of 65 are one of the most vulnerable groups for head injuries. Among seniors, falls are the most common cause of TBIs — a serious risk, but also preventable with a few key strategies.
Yet, despite how common TBIs are, many people don’t realize when they experience the “traumatic” incident, or underestimate its potential severity. At one time, a mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), which many know simply as a concussion, was thought to be a harmless event. Through extensive research, experts have now come to understand that even minor, repetitive brain injuries can have profound effects. These injuries can contribute to adverse neuropsychological outcomes, both acutely and long-term.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of a Concussion or Mild Brain Injury?
In the moment, a concussion might cause dizziness, ringing in the ears, blurred vision, and vomiting, all of which usually dissipate over a few days. But over time, that same injury or repeated injuries may contribute to ongoing symptoms. This condition is known as post-concussion syndrome, or PCS. Typical long-term symptoms include:
- Chronic headaches
- Trouble concentrating or thinking
- Memory problems
- Poor sleep
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Irritability
Why Some Brain Injuries Go Undiagnosed
Some people may not even connect an injury that happened years ago with their current symptoms. This can make it difficult to diagnose a TBI or post-concussion syndrome properly.
As a result, many people struggle with symptoms and have no clear path to recovery. The Brain Injury Association of America estimates that 5.3 million men, women, and children are living with a permanent TBI-related disability in the U.S. today.
But does the damage from a concussion or TBI have to be “permanent”?
Hope For Healing: Treatment for Post-Concussion Syndrome

Dedicated research into brain health has revealed a therapy that produces positive results in TBI and post-concussion syndrome cases. The medical community has long used hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) as a treatment for medical issues like wound healing, severe infections, and decompression sickness. But until recently, HBOT had not been explored by researchers much beyond those applications.
Studies conducted over the last two decades reveal that HBOT, when delivered using a specific protocol, may be able to repair areas of the brain that have been damaged due to TBI and concussion. This same protocol has also shown effectiveness in other conditions, including stroke, post-traumatic stress disorder, fibromyalgia, Lyme disease, and more.
How the Aviv Medical Program Supports Concussion and mTBI Recovery
To understand how HBOT works to address TBI and post-concussion damage, it’s important to know what changes occur in the brain during those injuries. There are two types of damage caused during a brain injury:
- Structural damage indicates a physical injury to the brain, such as bleeding.
- Metabolic damage describes changes at the cellular level that prevent the cells from producing energy.
Traditional scans like CT and MRI may not be able to detect metabolic damage, especially if an injury occurred years ago. More advanced scans, including like functional MRI and SPECT, are better able to identify areas of the brain, even when a concussion or TBI happened years earlier.
Research into the unique HBOT protocol used in the Aviv Medical Program indicates multiple potential changes in the brain:
- New blood vessel formation (angiogenesis)
- New and stronger neural connections (neuroplasticity)
- Growth of new neurons or brain cells (neurogenesis)
These neural, vascular, and cellular changes can translate into real-world improvements in several cognitive domains:
- Memory
- Executive function
- Attention
- Processing speed
- Spatial memory
- Motor function
Beyond hyperbaric oxygen therapy, the personalized Aviv Medical Program can also include cognitive exercises, physical therapy and physical training, nutritional coaching, and other interventions. Our board-certified physicians prescribe an individualized plan for each Aviv Clinics’ client, based on their physiology, condition, symptoms, and recovery goals. The results of HBOT, combined with complementary therapies, can lead to greater aerobic fitness, higher energy levels, improved sleep, and reduced pain. Overall, clients report a significant improvement in their quality of life after completing the program.
Regaining Your Brain Health After a Concussion

If you’ve ever been in a car accident, fallen off a ladder, or had “your bell rung” playing sports, you may have experienced a brain injury that has a deeper impact on your health. The Aviv Medical Program can help ease your symptoms. With our customized approach and evidence-based therapies, we’re helping people recover from brain injuries even years after the event.
If you or a loved one suspects a TBI or concussion has left lingering symptoms, contact us to learn more about how the Aviv Medical Program could change the rest of your life.
Last Update: July 17, 2025
Signs and Symptoms of Lyme Disease
Lyme disease is the most common tick-borne illness in the United States. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) receive approximately 30,000 official reports of Lyme disease annually, but recent CDC estimates suggest that approximately 476,000 individuals develop Lyme disease each year in the U.S. It’s imperative for people to recognize the early signs and symptoms to avoid Lyme’s long-term effects, which can be debilitating.
What Causes Lyme Disease?
Lyme disease is a relatively modern affliction. It was first identified in the U.S. in 1975, in the town of Lyme, Connecticut. Since its discovery, scientists have performed numerous studies to better understand the disease, how it is transmitted, and its biological impact on the human body.
Lyme is most commonly spread by deer ticks, primarily found in the Northeast, upper Midwest, and Northwest. Deer ticks are also known as black-legged ticks, Ixodes scapularis, or Ixodes pacificus. These ticks are very small, making them troublesome to see. Some are as tiny as a poppy seed.
These ticks carry the Lyme disease bacterium, Borrelia burgdorferi, which is a spirochete—a highly invasive bacterium. These bacteria quickly move through the skin and break into and out of blood vessels. The Lyme bacteria can even cross the blood-brain barrier. These bacteria are also difficult to kill—especially if left untreated in the very early stages of the infection.
Lyme Disease in Three Stages
There are three main stages of Lyme disease, and each has its own signs and symptoms. Initially, Lyme can manifest itself as a rash known as erythema migrans (EM). The rash expands over time, after the tick bite, sometimes reaching 12 inches or more across. It may feel warm to the touch, but the rash is rarely painful or itchy. Sometimes, the rash clears in the middle, resembling a bullseye. However, this bullseye indication doesn’t always appear. Acute signs, like EM, are key in identifying Lyme because it’s estimated that only about 17% of people recall being bitten by a tick.
Timing is crucial in this acute stage of infection, regardless of whether the individual develops a rash. When a person can identify a tick bite, clean the site right away with antibacterial soap and water, and notify their primary care provider, they may be able to cure the infection in 10-12 days.
Lyme progresses to the subacute stage when an infection goes unnoticed and thus untreated. Individuals may experience flu-like symptoms such as headaches, fever, and chills.
As time goes on, symptoms worsen into joint pain, swelling and other bodily aches, similar to arthritis. By this stage, people are in the “danger zone” of chronic Lyme disease.
Lyme can cause cardiac dysrhythmias, a condition in which the heart is not beating correctly. Cardiac dysrhythmia can eventually cause the heart to fail. Some Lyme patients may need a pacemaker to regulate their heart’s rhythm.
Because the Lyme disease bacterium, Borrelia burgdorferi, crosses the blood-brain barrier, neurological symptoms may result, such as:
- Confusion
- Brain fog
- Facial paralysis or drooping
- Severe head pain
- Visual disturbances
- Neck stiffness
- Intermittent pain in tendons, muscles, joints, and bones
- Episodes of dizziness or shortness of breath
- Heart palpitations
- Inflammation of the brain and spinal cord
- Nerve pain
- Numbness, tingling, or shooting pain in the hands or feet
Some individuals even report having an “out of body” experience, feeling they are in one place when they’re not, similar to a hallucination.
Testing for Lyme Disease
Chronic Lyme is difficult to identify and adequately treat because no definitive diagnostic test exists. Most Lyme disease tests are designed to detect antibodies that the body creates as it responds to the infection. But antibodies can take several weeks to develop, meaning that patients may test negative in the early stages of infection.
Specific immunological markers may reveal a reason for concern via blood testing. However, these markers can also indicate other types of infections, including other tick-borne diseases, viral, bacterial, or autoimmune diseases—all of which can result in false positive test results.
The most effective way to uncover Lyme is through a solid, thorough history, clinical examination, and a Lyme questionnaire.
Treating Lyme Disease
Traditional treatment for Lyme disease includes antibiotics, antivirals, and antifungal protocols. Treatment is challenging because spirochetes are extremely intelligent. Many bacteria contain plasmids, which are small, circular DNA molecules that can make bacteria resistant to antibiotic treatment. With Lyme, this process becomes heightened. Research has shown that the Lyme disease Borrelia burgdorferi species presents the most complex plasmid structure among known bacteria.
Spirochetes are so smart and fast that they communicate with other spirochetes, telling them to change various factors such as pH or temperature, or generate a new plasmid that will ultimately resist the treatment.
When one antibiotic treatment doesn’t work, physicians may try as many as 20-30 different types. Unfortunately, this can perpetuate the resistance and induce long-lasting molecular changes to the body’s microbiome. The immediate physiological effects plague patients daily, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. Serious, sometimes deadly, complications are associated with long-term antibiotic treatment.
Despite all these efforts, the spirochetes survive. Autopsy evidence reveals that spirochetes keep growing persistently, even after 15 years of antibiotic treatment. Given all the evidence, prescriptions may aid in alleviating some of the accompanying symptoms of Lyme, such as pain, depression, anxiety, and poor sleep, but they simply do not work effectively to eliminate the infection itself.
What to Do When Traditional Lyme Treatments Don’t Work
Multiple research studies have shown the positive benefits of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) in treating Lyme disease and its symptoms. The science behind this approach involves how spirochetes respond when exposed to oxygen: they die.
Individuals living with chronic Lyme disease who have undergone HBOT treatments and the Aviv Medical Program protocols report relief from symptoms like digestive distress, brain fog, joint pain, and overwhelming fatigue. Many have been able to return to the active lifestyle they have been missing for years.
HBOT and the accompanying protocols of the Aviv Medical Program will be increasingly valuable in the coming years. In the next decade, Lyme is projected to become a severe epidemic — particularly in the Northeast, upper Midwest, and Northwest.
If you or a loved one suspects chronic Lyme disease is at the root of troubling health issues, contact us to learn more about the Aviv Medical Program and its role in providing relief for Lyme patients.
Benefits of Intermittent Fasting for Visceral Fat, Longevity, and Metabolic Health
Intermittent fasting has become a popular dietary buzzword over the last decade, but it’s far from being a new concept. In prehistoric times, fasting was just a part of daily life. As hunters and gatherers, our ancestors often went long stretches without food between successful hunts. We’ve come a long way since then to discover the true scientific benefits of intermittent fasting.
The documented benefits of intermittent fasting as a dietary method also stretch back centuries. In the 1500s, nobleman Luigi Cornaro, made significant changes to his diet and lifestyle habits in his 40s to strengthen his “weak constitution.” He eventually lived to be 103 years old, a shock to his colleagues. Twenty years before his death, he chronicled his dietary changes for posterity.
Today, intermittent fasting is supported by extensive clinical research. In 2019, the New England Journal of Medicine published a landmark peer-reviewed paper on its health benefits. For many, intermittent fasting is more than a tool for weight loss. It’s also a viable approach to living longer, healthier lives.

What is Intermittent Fasting and Why Does It Work?
The human body operates with one goal in mind: survival. If you go 8-12 hours without food, your entire body is out of its primary energy source. You have no more stored glycogen, which provides energy. Your liver and muscle cells are empty, and your brain is screaming for sustenance. As a result, your body begins burning fat for energy instead. Specifically, it targets visceral fat, or the fat that surrounds our organs.
It’s important to note that not all fat stored in the body is “bad.” Humans need certain types of fat to promote healthy metabolism and optimal hormone levels.
However, visceral fat doesn’t hold those positive connotations. High visceral fat levels are linked to conditions like:
- Diabetes
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Arterial disease
- Certain types of cancers
By prompting the body to burn visceral fat, intermittent fasting may help reduce the risk of these conditions while also supporting metabolic health.
Scientific Benefits: Longevity, Inflammation Reduction and More
The research on intermittent fasting reveals its impact beyond weight loss. Additional benefits include improvements to:
- Thinking and memory
- Blood pressure
- Physical performance
- Type 2 diabetes
- Sleep apnea
Intermittent fasting may also have protective effects against certain cancers and promote longevity. One study reveals that 13 hours without ingesting calories reduces breast cancer recurrence. In laboratory rodents, intermittent fasting improved longevity by 15-20 percent.
Inflammation reduction is another benefit. Chronic inflammation plays a role in the development many serious conditions, such as:
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Arthritis
- Asthma
- Multiple sclerosis
- Stroke

The Easiest Diet? Real-life Benefits of Time-Restricted Eating
Aside from the health benefits, one of the best aspects of intermittent fasting is that it doesn’t require people to invest any extra time or money. It doesn’t require special foods, hours measuring and weighing your meals, or calorie counting. There are also no “off-limit” foods. You can still enjoy your favorite meals and snacks as long as you do so in moderation.
In truth, all intermittent fasting really takes is time. You already fast every night while sleeping, right?
A popular intermittent fasting schedule is 16:8, or fasting for 16 hours and feasting for eight. Your goal should be to fast for at least 13 hours a day, which is where the measurable health benefits take hold. However, there’s no detriment to switching up your schedule. Some days you may hit 13 hours, other days, you might aim for 16 or 18.
Consistently practicing intermittent fasting is more important than perception. You might fast for 16 hours on weekdays, then relax your schedule on weekends. This flexibility makes intermittent fasting easier to stick with long term.
That said, there is some risk in fasting for too long. For example, if you’re regularly hitting the 20-hour mark, you’ll likely start to lose muscle mass. The body can only absorb 30 grams of protein at a time. With a limited feast window, you may not be getting adequate protein intake.
Popular Fasting Schedules: 16:8, 5:2 and Alternate Day Plans
There are multiple different approaches to intermittent fasting. Some of the most common include:
- Time-Restricted Fasting. This approach works by limiting the daily window of feasting. For example, if you eat your first meal of the day at 10 a.m. and your last meal at 6 p.m., you’ve followed the 16:8 plan. Common ratios for time-restricted fasting include 14:10, 16:8, and 18:6.
- 5:2 fasting. In this strategy, individuals eat “normally” five days a week and fast for two days. On the fasting days, they restrict their calorie intake to one 500-calorie meal for women and one 600-calorie meal for men.
- Alternate Day Fasting. Using the same calorie intake as 5:2, fasting takes place every other day.
Time-restricted fasting is usually the best place to start, because you can ease into it by gradually shrinking your feast window. As you get more accustomed to fasting, you might venture into other methods to see if they work for you.
Intermittent Fasting Side Effects and Safety Considerations
Intermittent fasting is generally safe, but it isn’t for everyone. You should consult your doctor before changing your diet plan, especially if you live with one of these conditions:
- Diabetes. Diabetics should consult with their endocrinologist or diabetes educator before starting intermittent fasting. However, for people with insulin resistance, intermittent fasting may prevent diabetes from developing.
- Digestive issues. Some people experience constipation, which can occur especially if they don’t drink adequate amounts of water or eat enough high-fiber foods.
Of course, in the initial stages, one might experience some fatigue, hunger pangs, and possibly headaches. As with any lifestyle change, it takes persistence and time to adapt. Still, it’s critical to have a conversation with your healthcare provider if you’re curious about intermittent fasting’s effects.
Explore Nutrition Coaching and Health Support at Aviv Clinics
Intermittent fasting is a well-researched, low-effort approach to supporting physical health, cognitive performance, and longevity. Whether you’re aiming to lose weight, sharpen your mind, or reduce your risk of chronic disease, it’s a powerful tool—and it costs nothing to start.
At Aviv Clinics, nutrition coaching is one component of the personalized Aviv Medical Program. Our program incorporates physician-prescribed interventions, including a unique, evidence-based hyperbaric oxygen therapy protocol, to help you reach your health goals.
If you’re interested in exploring how Aviv Clinics can support your healthy living goals, we’re here to help.
Last Update: July 15, 2025.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for Stroke Recovery: Reignite Healing in the Brain
Stroke is a leading cause of serious long-term disability in adults, with nearly 800,000 Americans experiencing one each year. Whether it’s an ischemic stroke or a transient ischemic attack (TIA), recovery depends heavily on timely, effective treatment. Even with timely intervention, however, many survivors are left with lingering effects, like reduced mobility, impaired speech and vision, and cognitive challenges. While no treatment can reverse damage to dead brain cells, exciting advancements in stroke rehabilitation are showing promise, especially hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT). The Aviv Medical Program uses hyperbaric oxygen therapy for stroke recovery as part of a personalized, multidisciplinary treatment plan to help achieve measurable improvements, even years after a stroke.
What Happens to the Brain during a Stroke?
When a stroke strikes, blood flow to the brain becomes interrupted, causing death to brain cells due to loss of blood and oxygen. As many as two million brain cells die each minute a stroke goes untreated. Other cells become injured but don’t necessarily die off. Neurologists often describe them as being “stunned” in this area of the brain, known as the penumbra.
The combined damage from injured and necrotic (dead) brain cells results in both immediate and long-term symptoms such as:
- Limb weakness or paralysis
- Slurred speech
- Vision complications
- Balance issues.
Once brain cells (neurons) have died, they cannot be revived, which is why timely intervention is so critical. However, a growing body of research indicates that HBOT may help repair the injured or stunned cells, even years after the initial stroke
How Can Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) Support Brain Recovery?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is a type of therapy that uses pressurized chambers to allow individuals to breathe in 100% pure oxygen. The increased pressure in the hyperbaric environment allows for more oxygen to be dissolved in the blood and tissues. When administered using certain protocols, HBOT can raise oxygen levels in the body to about 17 times higher than normal. This allows oxygen to be delivered even to dormant cells, such as those injured by stroke.

How Does HBOT Help with the Post-Stroke Recovery Process?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) supports stroke recovery by increasing the amount of oxygen delivered to injured brain tissue. When administered using a research-backed protocol, HBOT has been shown to:
- Promote healing in stunned or dormant brain cells
- Stimulate the growth of new blood vessels (angiogenesis)
- Activate stem cells to support tissue repair
- Trigger neuroplasticity—creating new neural connections
- Improve cognitive, speech, and motor function in stroke survivors
These benefits are particularly valuable for stroke survivors.
Fluctuating Oxygen Protocol: The Aviv Approach to HBOT
Based on nearly two decades of peer-reviewed, published research, the unique HBOT protocol at Aviv Clinics deliberately and safely fluctuates oxygen throughout the HBOT session. Patients receive treatment in a multi-person suite, accompanied by a medical professional. The suite is filled with medical-grade air, and clients breathe 100% oxygen through a mask. Thus, when the mask is on, oxygen levels in the body are very high. But when the oxygen mask is removed so patients can breathe normal air, the body is deceived into sensing a low-oxygen state.
This fluctuation triggers the body to believe it has become hypoxic, and it shifts into repair and regeneration mode. Research shows that this HBOT protocol can prompt neurological recovery even years after an initial stroke.

Real Results: Stroke Survivor Improvements with HBOT at Aviv
Several studies have proven the benefits of using HBOT in post-stroke recovery. When this specific HBOT protocol is combined with the broader Aviv Medical Program, results can be life-changing. Stroke survivors treated at Aviv Clinics have reported:
- Restored speech and reading capabilities
- Improved motor function, even with partial paralysis
- Greater independence in performing daily activities
Some clients have improved from using a wheelchair to walking with a cane. Others have regained communication skills they thought were lost forever. Many say the biggest benefit is no longer feeling like a burden to their loved ones.
The Personalized Aviv Medical Program for Stroke
When incorporated into the Aviv Medical Program, the outcomes become even more impressive:
- Some Aviv clients have progressed from using wheelchairs to walking on their own or with an assistive device.
- Clients who have lost their ability to speak can make immense recovery strides.
- Many report that the biggest benefit is simply not being a “burden” on their loved ones.
The Aviv Medical Program is grounded in nearly two decades of rigorous clinical research and built around a highly personalized approach to treatment. We begin with an in-depth evaluation designed to uncover the sources of your cognitive and physical challenges after your stroke. After an in-depth review of your health history and a physical exam, your Aviv Clinics physician may also recommend:
- Advanced brain imaging (MRI and/or SPECT)
- Body composition analysis
- Neurological and neurocognitive evaluations
- Physical and functional performance testing
From there, your dedicated medical team will design a customized treatment plan tailored to your unique condition, symptoms, health history, and recovery goals. Depending on your needs, your Aviv Medical Program may include:
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy using our unique, scientifically-backed protocol
- Cognitive exercises to support brain performance
- Physical training and physical therapy
- Nutritional coaching to optimize energy, focus and healing
Learn more about the program>>
When to Begin Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy After a Stroke
Aviv Clinics generally recommends waiting 3-6 month after a stroke before beginning hyperbaric oxygen therapy for stroke recovery. This allows for the brain’s natural healing process to stabilize before starting intensive therapy.
The sooner stroke survivors act after the post-acute stage, the better. Research shows that the greatest gains typically are seen when treatment begins less than four years post-stroke. That said, scientists have documented success even in clients who began treatment up to 10 years into their stroke recovery.
Expected Timeline to See HBOT Results
Most people see improvement from the Aviv Medical Program within 8-12 weeks. However, the individualized nature of the Aviv Medical Program means that outcomes and timelines vary. Our physicians prescribe a personalized treatment plan based on thorough assessments, your symptoms and medical history, and your treatment goals. This helps to ensure meaningful, measurable progress as you complete the program.
For most clients, here’s what the Aviv Medical Program looks like
- Step 1: Assessment— A set of assessments recommended by your Aviv Clinics physician to set baselines and establish your program.
- Step 2: Treatment— Based on the assessment, we develop a customized routine that can combine hyperbaric oxygen sessions with other types of personalized interventions. In most cases, stroke patients complete treatment over the course of 12 weeks.
- Step 3: Analysis— At your request, our team can repeat the tests from your initial assessment and measure your progress. A post-assessment will also enable our physicians to make recommendations for ongoing recovery.
Client Story: Keren’s Post-Stroke Transformation
After suffering an ischemic stroke, Keren Trabelsi, a busy executive, was left with cognitive issues and paralysis on the left side of her body. Daily tasks grew more difficult, which left her feeling defeated.
Overwhelmed and discouraged, Keren discovered the Aviv Medical Program. Following three months of hyperbaric oxygen therapy for stroke recovery alongside other interventions, Keren regained her ability to walk comfortably, type, and enjoy mental challenges like Sudoku once again. In her words, treatment at Aviv is “…like driving a Ferrari on the road to recovery versus driving like an old beaten-up car….”
Reclaim Brain & Body with Aviv’s Scientifically Backed Stroke Program
Stroke recovery doesn’t need to end with basic rehabilitation. The Aviv Medical Program offers a comprehensive, scientifically backed pathway to better physical and cognitive performance.
If you or a loved one is living with post-stroke challenges, our team is here to help. As the largest and most advanced civilian hyperbaric medicine treatment center in the United States, our expert clinical team is ready to discuss how the Aviv Medical Program may benefit you or your loved one. Contact us to learn more.
Last Updated July 14, 2025
Types of Stroke and Their Symptoms: What You Need to Know
Each year in the United States, nearly 800,000 people suffer strokes. This means that every 40 seconds, someone in the United States has a stroke, while an American dies from a stroke “every 3 minutes and 14 seconds.” Strokes aren’t always equal in severity, but there is still a significant impact on brain cell damage, death, and overall brain performance. These effects manifest in various physical and cognitive ways. Learn the types of stroke and symptoms to watch for, and discover and how the Aviv Medical Program can play a part in a post-stroke rehabilitation journey.
Types of Stroke: Ischemic, Hemorrhagic, and TIA Explained
There are three primary types of strokes:
- Hemorrhagic: Caused by bleeding in or around the brain
- Ischemic: Caused by a blockage like a blood clot, which cuts off blood supply to the brain
- Transient ischemic attack (TIA): A mini-stroke in which blood blockage is temporary or short-lived
Ischemic strokes comprise about 87% of all strokes, a number that also encompasses TIAs. Hemorrhagic strokes make up the remaining 13%.”
What Is a TIA? Understanding Mini-Stroke Symptoms and Risks
Though a TIA is often referred to as a mini-stroke, it’s vital to understand that such an event can be just as damaging as a traditional stroke in the long run. The number one risk factor for having a stroke is a previous stroke, including a TIA.
While the definition of a TIA has evolved over the past two decades, most neurologists now diagnostically classify a TIA as a type of stroke, and not just an “attack,” because it still represents ischemic activity.
If you experience a TIA, you should take it seriously. Think of it this way: maybe you didn’t get fatally shot, but you still got hit.
Stroke Symptoms: How to Recognize the Warning Signs
With a stroke, timely intervention is critical. According to experts, an individual can lose nearly 2 million brain cells in each minute following a stroke, which further heightens the risk of permanent brain damage, disability, and death. So, everyone must know the signs and symptoms of a possible stroke.
You may be familiar with the FAST acronym for identifying a stroke. Regardless of the types of stroke, facial drooping, arm weakness, and speech difficulty are three of the best-known symptoms, the FAST method may miss up to 14% of stroke cases. A recent article in the journal Stroke suggests the wide adoption of the mnemonic BE-FAST.
- B: Balance. Is the person struggling with balance or coordination?
- E: Eyes. Has their vision suddenly changed? Do they have blurring, double vision, or vision loss?
- F: Facial drooping. Is the person able to smile normally?
- A: Arm weakness. Can the person raise both arms to equal height? Or does one drift downward?
- S: Speech difficulty. Are they slurring their words or having trouble communicating thoughts?
- T: Time is tissue. Call 9-1-1 immediately.

Lesser-Known Stroke Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore
While those mentioned are the classic stroke symptoms most often discussed by physicians and stroke awareness advocates, additional signs may point to stroke.
For example, nausea, dizziness or vertigo, confusion, and visual changes may also be indicators. Sometimes, if the TIA affects the frontal-temporal lobe, a person might have a sudden personality change.
Ultimately, any sudden change should be considered a stroke possibility. Again, the highest risk factor for stroke is a previous one, so the older a person gets, the more likely they are to develop a stroke.
However, children, teenagers, and young adults are not immune. There may have been anatomical factors while in the womb, heart arrhythmias, or external exposures such as drugs and alcohol. In some scenarios, extreme stress can bring on a stroke.
Why Fast Stroke Response Saves Brain Cells
If treatment takes place within three hours of symptom onset, there is a much greater chance that an individual will recover with little or no disability. If intervention is delayed, there are still some options available:
- Thrombolysis: Advancements in ischemic stroke treatment include a method called intravenous thrombolysis (IVT), which involves medicine that works as a clot-buster to restore blood flow to the brain. It is administered via an IV, so no surgical intervention is required.
However, this treatment must be given within the first four-and-a-half hours of stroke occurrence. If that window closes, the patient is typically not eligible to receive the medication unless indicated by imaging.
- Thrombectomy: Another option is mechanical thrombectomy. This non-invasive procedure involves inserting a catheter into the arteries, navigating to where the clot is, and retrieving it. Studies note, “mechanical thrombectomy significantly improved functional independence and appeared to be cost-effective compared to IVT alone.”
- Combined approach: Scientists have also developed an approach that combines medicinal thrombolytic treatment with mechanical thrombectomy. Research indicates that integrating the two in a primary stroke center has benefits comparable to care in a comprehensive stroke center, “with no statistically significant difference.”

What to Do When Stroke Symptoms Appear
As soon as you experience any symptoms of stroke, call 9-1-1. Don’t drive yourself to the emergency room. Instead, wait for the EMTs. In most cases, emergency response workers can start making critical assessments and relay the stroke response team waiting at the hospital.
It can’t be emphasized enough: a timely response means everything. Once the stopwatch begins, you have very little time to act to optimize outcomes.
How to Lower Your Risk of Stroke with Lifestyle Changes
The CDC reports that “you can help prevent stroke by making healthy lifestyle choices.” Although some strokes are caused by factors beyond your control, you can take ownership of your health and longevity by incorporating these small changes:
- Eat more fruits and vegetables. Consider transitioning to a Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay (MIND) diet, which can offer anti-inflammatory and cognitive benefits.
- Get regular exercise. We recommend 30 minutes of exercise three days a week at a minimum. Physical activity releases endorphins, helping you feel good. Regular exercise can lower your blood pressure, reducing a common stroke risk factor. Consider pursuing an activity you thoroughly enjoy to stay motivated.
- Find helpful ways to cope with stress. Stress can negatively impact the brain. Look for ways to manage stress, such as therapy or counseling, interacting with loved ones regularly, or meditating. Avoid smoking or consuming alcohol to cope with stress, as these behaviors can increase your risk of stroke.
These are all simple ways to invest in your health to avoid preventable issues in the future.
Can Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy Help After a Stroke?
If you or a loved one has had a stroke with cognitive or physical after-effects, hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) has emerged as a potential rehabilitation option. HBOT can elevate oxygen levels in the blood up to 20 times higher than normal.
Decades of research note that the impact HBOT has on the mind and body can lead to significant neurological improvements in post-stroke patients, even at chronic late stages. These findings offer hope for individuals who have experienced strokes months or even years ago.
Keep in mind that HBOT protocols and types of chambers used across clinics will vary. The studies above used a specific HBOT protocol, so it’s essential to do your research to find a HBOT clinic that is right for you.
Post-Stroke Recovery with the Aviv Medical Program
The scientifically backed hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) protocol used in the Aviv Medical Program may help repair and regenerate the brain after a stroke. Our unique HBOT protocol includes fluctuating oxygen levels during sessions. This evidence-based method not only floods tissues with much-needed oxygen but sparks a physiological reaction that initiates the body’s innate self-healing mechanisms.
Based on your condition, symptoms, medical history, and recovery goals, our physicians prescribe a personalized Aviv Medical Program, which may include hyperbaric oxygen therapy alongside other interventions, including:
- Cognitive exercises
- Physical training
- Physical or occupational therapy
- Nutritional coaching
- Other interventions as prescribed
The Aviv Medical Program embodies a customized approach to each patient’s health program. Learn more about our research and how you can return to optimal health after a stroke.
Start Your Stroke Recovery Journey at Aviv Clinics
Aviv Clinics’ research-backed program has helped thousands of patients elevate their quality of life after different types of stroke. If you or your loved one suffers from debilitating conditions, our diverse medical team is ready to lend a hand.
Contact us to learn more about the Aviv Medical Program and how it can benefit post-stroke recovery.
Last Updated July 14, 2025
The Effect of Coffee on Brain Health
Pour-over, solo, drip, French-pressed—however you enjoy your coffee, it may do more than just help you get going in the morning. Research suggests that drinking coffee may protect against a variety of health conditions, as long as it’s consumed in moderation.
For decades, coffee had a poor reputation due to early studies that labeled it a carcinogen and linked it to an increased risk of heart disease. But recent research shows that drinking coffee, including decaffeinated coffee, may provide a variety of health benefits when enjoyed in moderation.
Why Coffee Matters for Your Brain
Some of coffee’s health benefits are commonly known, including that it boosts metabolism and increases energy levels. But coffee may also deliver lesser-known, but potentially more important advantages for the brain. These include:
- Enhancing brain function
- Lowering the risk of developing dementia and Alzheimer’s disease
- Decreasing the risk of stroke and depression.
Beyond brain health, moderate coffee consumption has been linked to reduced risk of some cancers, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.
How Caffeine Enhances Focus and Alertness
Caffeine is just one of about 1,000 chemicals found in coffee beans, but it is the best known. As a stimulant, caffeine delivers a boost of energy and helps provide focus. It locks into the adenosine receptors in the brain, which cause drowsiness, and counteracts the sleepiness response by blocking the function of the receptors. Instead of feeling drowsy, caffeine stimulates the brain’s production of norepinephrine and dopamine, which is what leads to increased focus and alertness.
Beyond Caffeine: Antioxidants and Polyphenols
But caffeine isn’t the only beneficial component. Coffee also contains beneficial polyphenols and antioxidants, which fight inflammation and protect against some diseases.
Polyphenols are organic compounds with anti-inflammatory properties that have the potential to prevent or reduce the risk of certain cancers and other chronic health conditions. Some polyphenols may protect against neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s. Additionally, polyphenols may also help regulate metabolism, weight, and cellular function.
Other beneficial components in coffee include:
- Vitamins B1 (thiamine), B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin) and B5 (pantothenic acid)
- Folate
- Manganese
- Potassium
- Magnesium
- Phosphorus.
Coffee beans may also support gut health by offering prebiotic and probiotic properties once ground and brewed.

Coffee’s Impact on Memory and Dementia Risk
While coffee has many health benefits, it can also have some negative effects. For example, it can:
- Disrupt sleep
- Cause anxiety or agitation
- Lead to caffeine dependence
- Trigger withdrawal symptoms (headache, fatigue, brain fog, and irritability) when abstaining
Moderating consumption is key to enjoying its benefits.
Balancing the Benefits: Moderation
Like most things in nutrition, balance matters. Coffee is a healthy beverage when consumed in moderation. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends no more than about 400 mg of caffeine, or about 2-3 12-ounce cups. Too much, especially in the afternoon or evening, can interfere with sleep quality and may create feelings of anxiety.
Brewing Smart: How to Maximize Health Benefits
While coffee has many health benefits, its value can be undermined by added sugars, creamers, or flavored syrups.
“The extra calories, sugar, and saturated fat in a coffee house beverage loaded with whipped cream and flavored syrup might offset any health benefits found in a basic black coffee.” – Harvard School of Public Health

Brewing methods also matter when it comes to your health. Using a paper filter or selecting coffee pods with built-in filters helps prevent the passage of unhealthy chemicals present in your brew. Some of these chemicals can raise levels of LDL, also known as the “bad” cholesterol.
Support Brain Health With Personalized Nutrition
A daily cup of coffee may support brain function, but it’s just one small part of a much bigger picture. At Aviv Clinics, we take a comprehensive, science-backed approach to brain health and performance. Our personalized treatment plans address cognitive and physical health with a cutting-edge hyperbaric oxygen therapy that can be combined with other evidence-based therapies. These include cognitive training, nutritional guidance, and physical performance coaching to help optimize both your mind and body.
Whether you’re experiencing early signs of cognitive decline or simply want to stay sharp as you age, our team of clinical professionals is here to help.
Discover how the Aviv Medical Program can support your brain health goals—today and in the years to come. Contact us to learn more.
Last Update: July 11, 2025
Mental Health Benefits of Golf: Boosting Mood, Reducing Anxiety and Building Connection
Since the COVID-19 pandemic, we’ve all become more aware of mental health challenges, the importance of addressing them, and the various ways they can be mitigated. Uncertainty, loss, and isolation have contributed to higher instances of depression and anxiety. Exercise and socializing are two ways to help maintain good mental health and reduce the risk of depression and anxiety.
The mental health benefits of golf offer a great way to easily combine exercise and socializing and support your mental health. Here are three primary reasons hitting the course is good for your brain.
How Golf Helps Depression and Anxiety
You may have heard of a ‘runner’s high.’ Many runners experience an exhilarating feeling during a great race or even during an everyday jog. However, running isn’t the only way to release endorphins, the brain’s “feel-good” neurotransmitters. Any form of exercise, including golf, can produce these mood-boosting chemicals.
For women, this can be particularly important. Many experts estimate that women are nearly twice as likely as men to be diagnosed with depression. The number could be even higher for those who suffer from depression, but do not have a formal diagnosis.
In an Australian study, researcher Kristiann Heesch looked at the effect of exercise on women’s depression. The results of her study showed that women who averaged 150 minutes of moderate exercise (golf, tennis, aerobics classes, swimming, or dancing) or 200 minutes of walking every week, had more energy, were more social, and felt better emotionally. These same women were not as limited by their depression, even three years after the study.
Endorphins also help ease anxiety, which is the most common mental health concern in the United States. According to data from the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI), over 40 million adults in the U.S. (19.1%) have an anxiety disorder.
The exposure to sunshine when playing golf also has mental health benefits. Research has linked vitamin D deficiency with instances of depression and other mental health struggles. Even a cloudy day on the golf course provides the sun exposure required to optimize your vitamin D levels.

Golf as Stress Relief and Green Exercise
Most people encounter periods of stress in their lives. However, when stress becomes chronic, it can affect other components of health.
The National Institute on Mental Health (NIMH) reports that repeated stress can disrupt the functioning of the immune, digestive, cardiovascular, sleep, and reproductive systems. Even more cause for concern, the continued strain that stress places on your body may contribute to serious health problems, such as heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, and mental illness.
Chronic stress also negatively impacts the brain through memory problems, and weakened mental health. Stress can lead to neural atrophy, or actual shrinking of the brain.
The restorative impact of the endorphins from a round of golf, along with the meditative nature of the focus it requires may help reduce stress. Additionally, exercising outdoors, or “green exercise,” is actually better than indoor exercise when it comes to stress reduction.
Shedding your tensions during the course of playing nine or 18 holes can leave you feeling calmer, clearer, more focused, and ready to manage both daily and extraordinary challenges in your life.
Golf for Social Connection and Loneliness
Humans are naturally social beings. Although we’re not all social butterflies, interaction with others has been shown to improve overall health and well-being. This is one of the reasons so many individuals suffered with mental health concerns during the COVID pandemic: being forced to isolate themselves from friends and family for weeks or even months at a time. Loneliness is a factor in poor mental health outcomes.
Research has revealed that person-to-person interaction triggers the nervous system to release a combination of neurotransmitters that regulate the body’s response to stress and anxiety. Dopamine is another feel-good chemical produced by the brain, which has a compounding effect on one’s mental health.
“It’s part of our reward center, and when our brain produces dopamine in response to what we do, we feel good and want to do more of whatever it is that’s making us feel so mentally healthy. That, in turn, leads to even more dopamine production,” explains Tanya J. Peterson, NCC, DAIS, a mental health educator.
Playing golf with your friends, spouse, or colleagues can help reap these socialization benefits. Aviv Clinics clients already enjoy the camaraderie naturally fostered by their hyperbaric oxygen therapy sessions in our state-of-the-art HBOT suites. Golf games provide more opportunities for socializing and improving their overall experience.

Supporting Brain Health Beyond the Golf Course
The clinical team at Aviv Clinics understands that good mental health isn’t just about what happens in your mind. Our mental health is also shaped by what we do with our bodies. Whether it comes from golf or another source, physical activity, cognitive stimulation, social connection, and time outdoors all play a role in supporting a healthy, resilient brain.
That’s why Aviv’s personalized treatment plans can be custom-designed to support both brain and body performance. Our goal is to help clients feel more energized, focused, and emotionally well. Whether it’s getting back to your favorite activities like golf or feeling more present and connected with loved ones, our multidisciplinary team can help you achieve your cognitive and physical goals.
If you’re ready to take a proactive approach to your mental wellness and cognitive health, we invite you to learn more about how the Aviv Medical Program can help.
8 Questions to Ask Before Starting Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is growing in popularity, as recent research has highlighted its ability to improve cognitive performance, physical recovery, and even potentially reverse aging biomarkers. But it’s important to understand that not all HBOT programs are created equal. From hospital wound care clinics to medi-spas promising to heal anything and everything, the types of HBOT available today vary widely in safety, science, and effectiveness. No matter where you’re considering treatment, there are important hyperbaric oxygen therapy questions you should ask first.
As more HBOT facilities open around the United States, it has become increasingly important to understand the differences and identify the option best able to meet your health goals and needs. As the largest and most advanced civilian HBOT facility in the nation, Aviv Clinics encourages you to educate yourself prior to treatment with hyperbaric medicine. Before you commit to a treatment plan, ask these seven questions to ensure the program aligns with your goals and delivers meaningful results.
1. What Type of Hyperbaric Oxygen Chamber Will I Be Using?
There are two main types of hyperbaric oxygen therapy chambers: monoplace and multiplace. Monoplace chambers treat one person at a time in an enclosed tube, while multiplace chambers are larger and accommodate multiple patients comfortably.
- Monoplace chambers are the most commonly used type of chamber and are frequently found in hospital burn units or wound care facilities. Patients typically recline in the tube while it is pressurized with 100% oxygen. Monoplace chambers are sometimes referred to as “Michael Jackson” tubes because the singer was once pictured inside one on the cover of the National Enquirer tabloid.
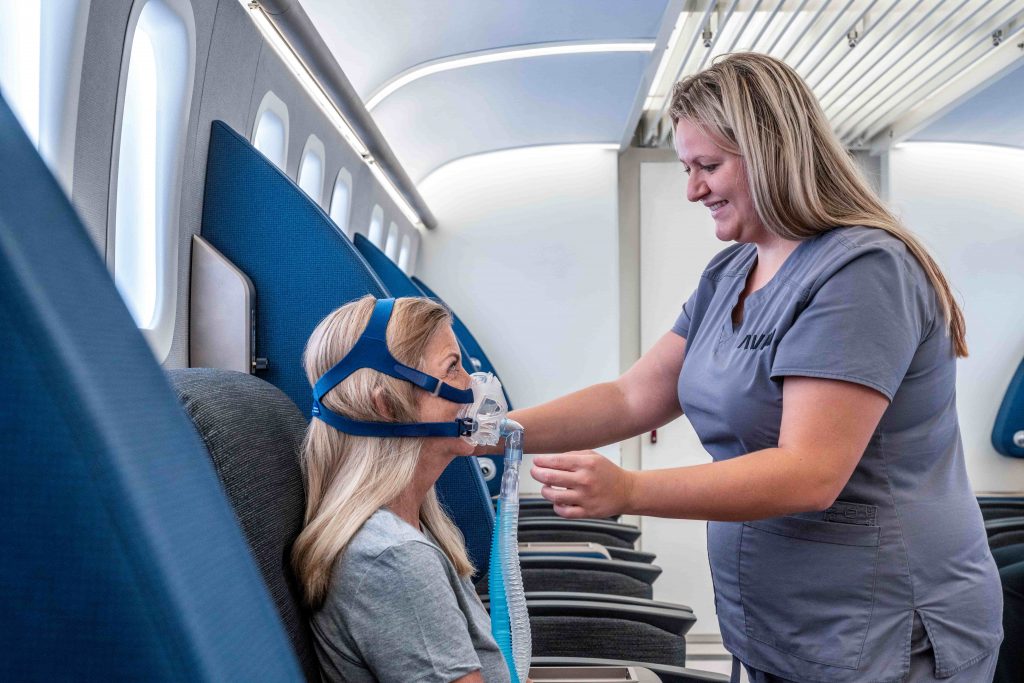
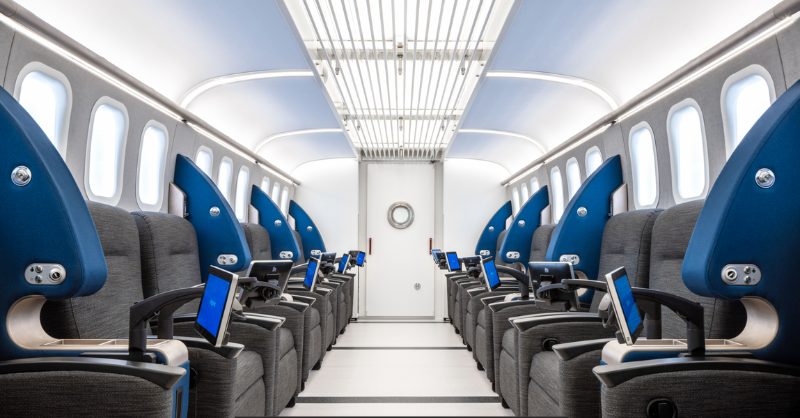
- Multiplace chambers, like the hyperbaric suites used at Aviv Clinics, are spacious, comfortable rooms that accommodate multiple people at once. Aviv’s suites resemble a first-class airplane seat, with comfortable seating, personal entertainment tablets, and a medical team member inside the chamber during every treatment. Instead of being pressurized with 100% oxygen, these suites are pressurized with medical-grade air, and patients breathe oxygen through a specialized mask.
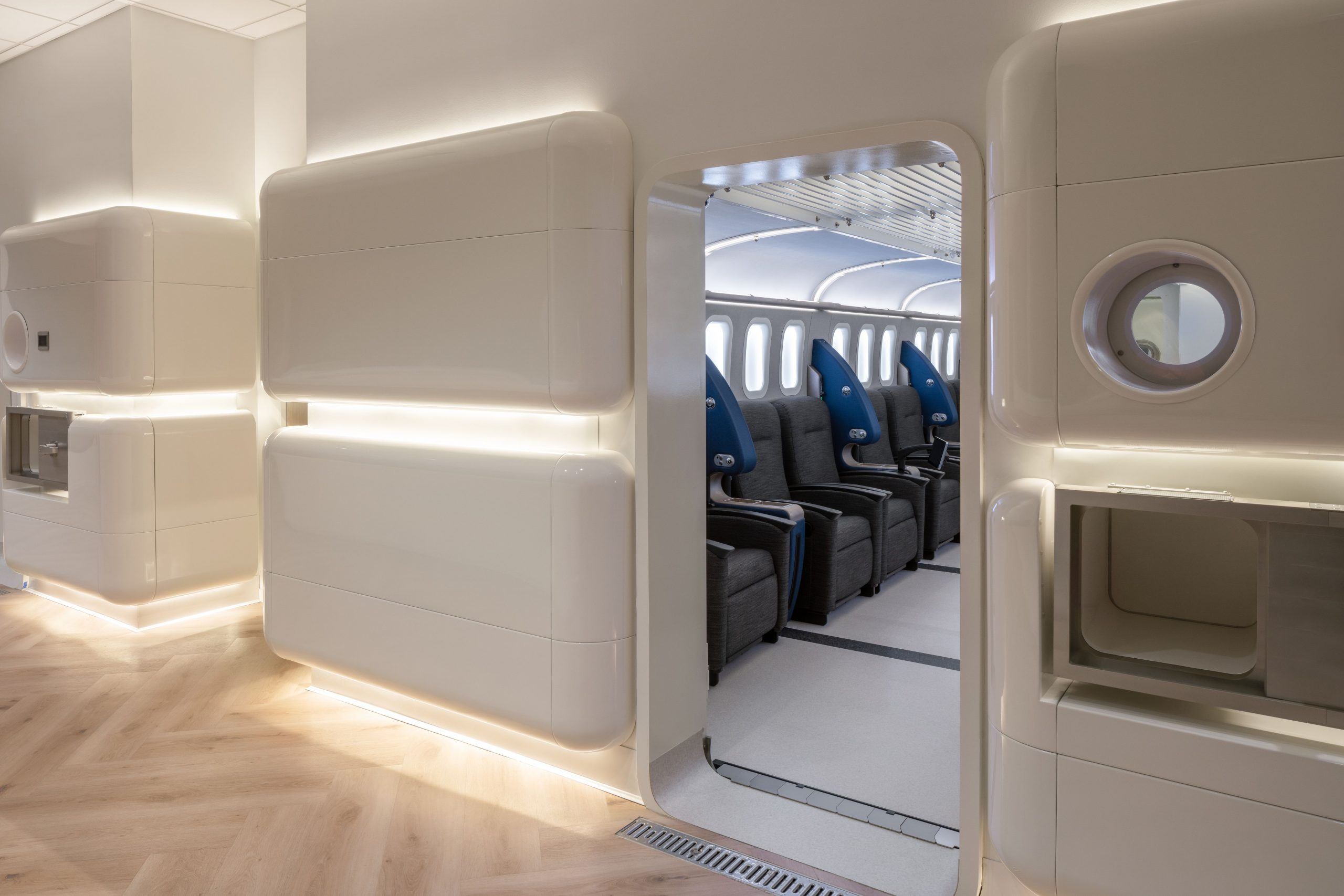

Aviv Clinics – Multiplace HBOT suite
What about soft-sided “mild” chambers?
A growing number of people are asking this hyperbaric oxygen therapy question, as many clinics tout the use of soft-sided “mild HBOT” chambers. However, these portable bag chambers are only approved for treating altitude sickness. They also operate at much lower pressures than hard-sided monoplace and multiplace chambers, limiting their therapeutic effect. Additionally, many clinics that offer “mild HBOT” often don’t meet the rigorous regulatory or fire safety code requirements for HBOT facilities.
2. What Conditions or Goals Does This HBOT Program Support?
HBOT can be used for a wide range of medical and wellness goals. Some clinics treat only acute wounds or infections, while others, like Aviv Clinics, offer research-backed programs that address cognitive decline, brain injury, PTSD, and more. Choose a clinic aligned with your specific condition or health objective.
Traditional HBOT facilities only treat acute conditions like gangrene, infections, burns, or decompression sickness. HBOT has been used for decades to treat these “on-label” conditions, which are typically urgent, treated at hospitals, and covered by insurance. In these instances, the number of HBOT treatments can be as few as one or two sessions.
Other facilities offer spa-like experiences, providing “wellness” dives without a clear protocol or clinical oversight.
In contrast, the research-backed Aviv Medical Program treats conditions that affect brain and body function. These include:
- Age-related cognitive and physical decline
- Stroke recovery
- Traumatic brain injury (TBI) and post-concussion syndrome
- PTSD
- Fibromyalgia
- Long COVID
- Lyme disease
- Chronic carbon monoxide poisoning
- Athletic performance issues
- Surgical recovery
3. Is the HBOT Protocol Backed by Scientific Research?
Many facilities offer hyperbaric oxygen therapy without peer-reviewed evidence or standardized protocols. Ask whether the treatment is rooted in science, and how the facility’s protocols compare to those used in the clinical trials. Every treatment you choose can affect your body positively or negatively, so doing your research and choosing a reputable clinic is paramount.
The pressure and length of treatments, as well as the oxygen dosage used in Aviv’s HBOT treatments, are the result of peer-reviewed scientific research. Aviv Clinics’ HBOT treatment protocol is based on nearly two decades of rigorous, published research. It was developed at the Sagol Center for Hyperbaric Medicine and Research, the world’s most advanced facility of its kind. The Aviv Protocol is uniquely designed to spark the body’s innate capacity for regeneration using oxygen fluctuation techniques, a method known in the scientific community as the hyperoxic-hypoxic paradox. In clinical trials, this protocol has proven to stimulate stem cell activity, reduce inflammation, and improve blood flow in the brain and tissues.
Notably, this protocol is difficult to replicate in single-person monoplace chambers and is not possible to administer in low-pressure “mild” chambers.
4. Who Makes Up the Clinical Team Supporting the HBOT Program?
An important hyperbaric oxygen therapy question is to ask about the type of expert on-site support available for treatment and guidance. Some clinics operate more like spas, with minimal or no clinical oversight by an on-site physician. Others focus narrowly on wound healing, with limited scope for treating complex or neurological conditions.
At Aviv Clinics, clients have access to a multidisciplinary team that includes:
- Hyperbaric physicians
- Clinical psychologists and neuropsychologists
- Physical therapists
- Physiologists
- Nutrition specialists
- Nursing professionals
5. Will Medical Staff Be Present During My HBOT Sessions?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is a medical treatment, so professional oversight and support during your sessions are critical. Some facilities and spas offering mild HBOT don’t even have a physician on site during treatments, or choose to monitor clients remotely via video feed.
Aviv Clinics offers a medically supervised HBOT experience:
- A nurse or other medical professional is inside the multiplace suite to provide care during every session
- A trained hyperbaric technician monitors each session from a control console next to the HBOT suite
- A physician is on site at all times during hyperbaric treatments.
Your safety and comfort are always top priorities.
6. What Pre- and Post-Treatment Assessments are Included?
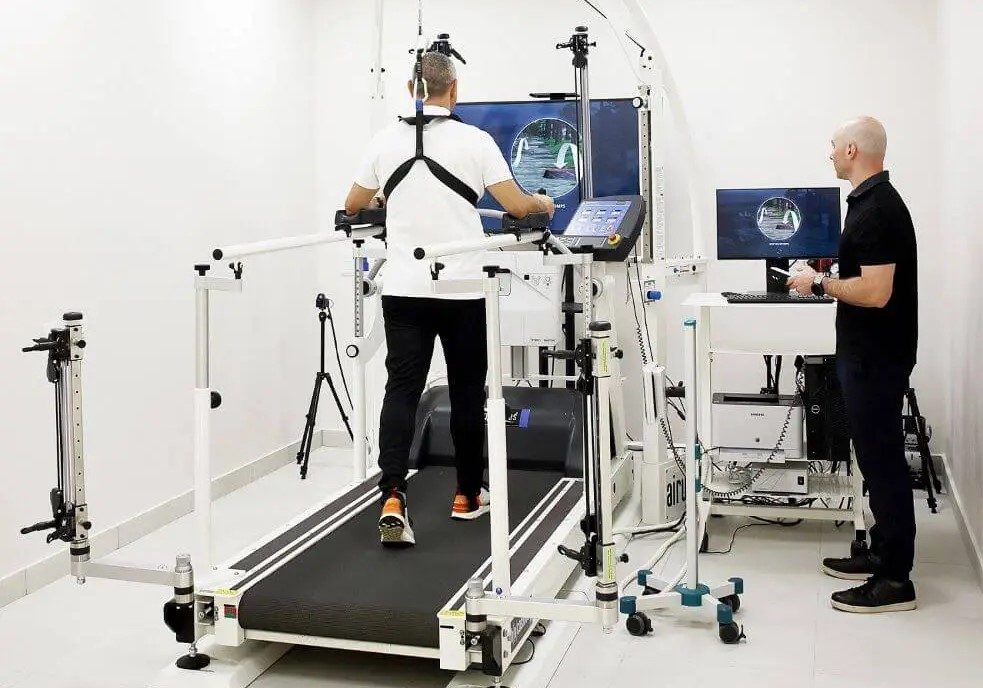
If a clinic doesn’t offer detailed assessments before and after treatment, there’s no objective way to track your progress. At a minimum, your provider should conduct a detailed medical history and physical examination and a chest x-ray before hyperbaric treatment. Depending on your individual needs, you may also need blood work or heart and lung function testing to determine your suitability for the treatment.
In addition to these assessments, the Aviv Medical Program can include the most comprehensive battery of pre- and post-treatment evaluations available.
At your request, these cognitive and physical tests can include:
- Extensive blood panels
- High-resolution brain imaging with MRI or SPECT
- Cognitive testing to measure memory, attention, and other cognitive domains
- Cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET)
- Body composition analysis
- Gait, balance, and overall motor function assessment
- Stem cell count and assessment of aging biomarkers
These assessments help define your health goals, guide your physician-prescribed treatment plan, and track measurable improvements.
7. Will I Receive a Detailed Report of My HBOT Progress?
Too often, clients leave HBOT clinics with no clear understanding of their results. Some facilities that work on a session-to-session basis may only provide minimal or per-visit tracking. Others may not offer results at all.
While some of our clients are perfectly happy with simply “feeling better,” others prefer a detailed before-and-after report. For those clients, we offer in-depth post-treatment reporting. Depending on your condition or reason for treatment, this report may track changes in:
- Physical health
- Cognitive performance
- Brain imaging
- Aging biomarkers
- Cellular health
- Condition-related metrics
Clients review their progress one-on-one with their Aviv Clinics physician, who explains and interprets the data and provides next steps.
8. Will The HBOT Clinic Coordinate With My Physician?
Some hyperbaric clinics operate outside the traditional medical system and don’t communicate with your personal healthcare team. If you’re working with a physician, specialist, or other provider, it’s important to choose an HBOT program that can integrate with your broader care plan.
At Aviv Clinics, we consider ourselves part of your overall care team. With your permission, we’ll coordinate directly with your existing physicians, share your assessment data and progress reports, and provide pre- and post-program evaluations for your permanent medical record.
Some clients are hesitant to tell their doctors that they’re exploring HBOT or other nontraditional therapies, but Aviv Clinics encourages transparency. In fact, many physicians are excited when they learn about the science behind our program and the measurable improvements their patients experience. We believe collaboration leads to better outcomes, and we’re here to support your health journey from every angle.
The Bottom Line: Not All HBOT is Equal
Before you invest time and money, make sure you know what you’re getting by asking these hyperbaric oxygen therapy questions. Your HBOT treatment protocol should be scientifically validated, supported by a caring, expert medical team, and offer a full range of assessments to show your progress.
This comprehensive approach allows Aviv Clinics’ clients to improve memory, regain physical stamina, and live with greater clarity and resilience.
Contact us to learn more about the Aviv Medical Program and how it can benefit you.
Last Update: July 10, 2025