Intermittent Fasting Chart: Methods & Timing Guidelines


Your brain orchestrates numerous systems that shape your overall vitality. From sunrise to sunset, these systems naturally cycle through rhythms of activity and rest, repair and renewal. While conventional wisdom often focuses on what to eat to fuel the mind and body, intentionally timing meals may be key to enhancing these restorative cycles.
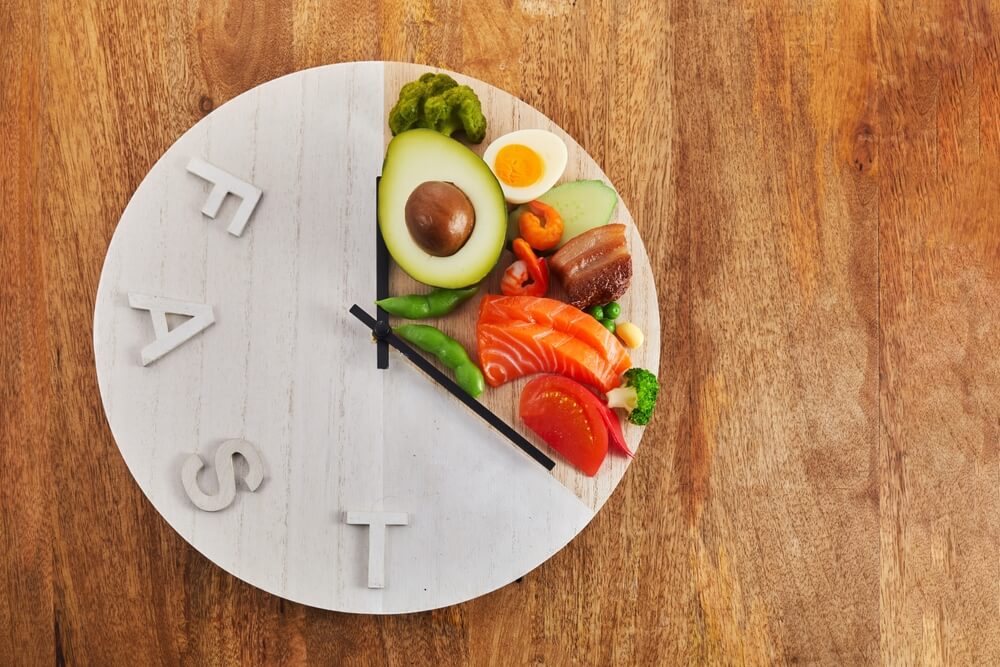
This is the essence of intermittent fasting — a structured approach to eating that harmonizes nutrition with innate rhythms to support both brain function and healthy aging. When you fast, your body activates vital repair mechanisms.
Finding your ideal rhythm can take exploration. The intermittent fasting chart below outlines different ways to incorporate these restorative periods into your routine and boost brain health.
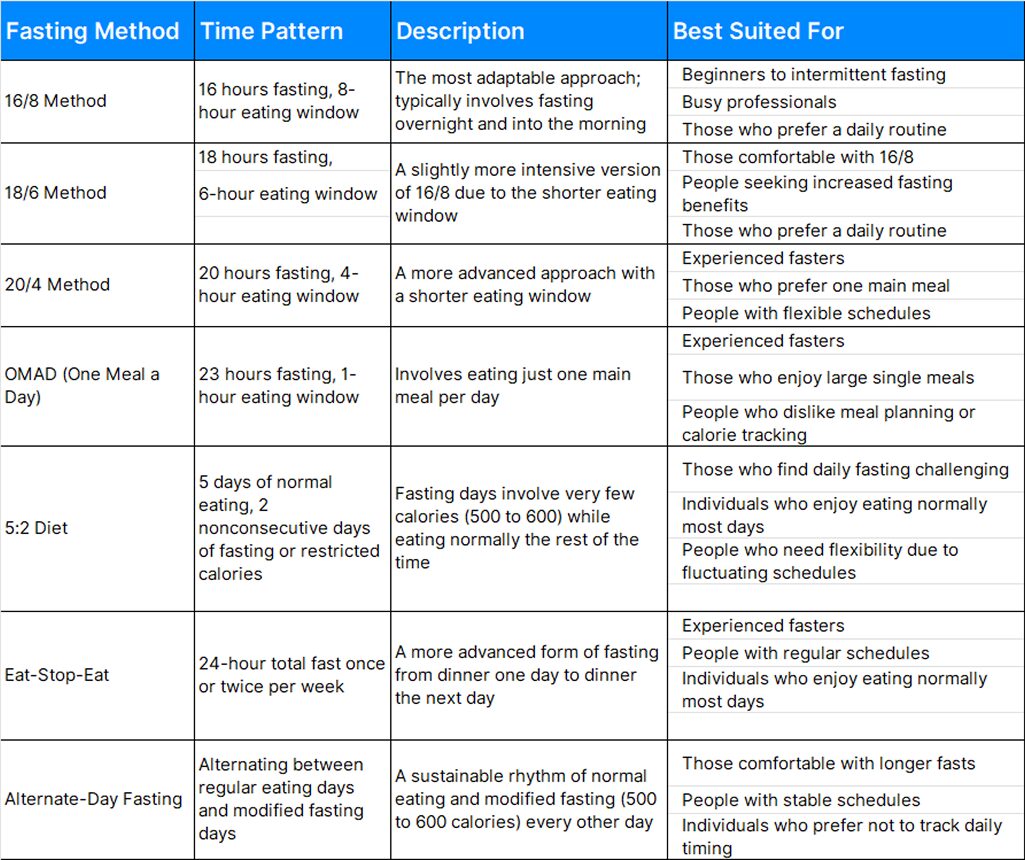
Intermittent Fasting Chart: Popular Methods
There are several popular approaches to intermittent fasting. Many people begin with 16/8 fasting, as it’s adaptable and straightforward. Listen to your body and adjust as needed — you can always explore longer fasting periods as you become more comfortable.
Note: Before starting any fasting regimen, especially if you have any health conditions or are taking medications, consult with your health care provider to ensure the approach you choose is safe and appropriate for your individual circumstances.
Intermittent Fasting Meal Plans
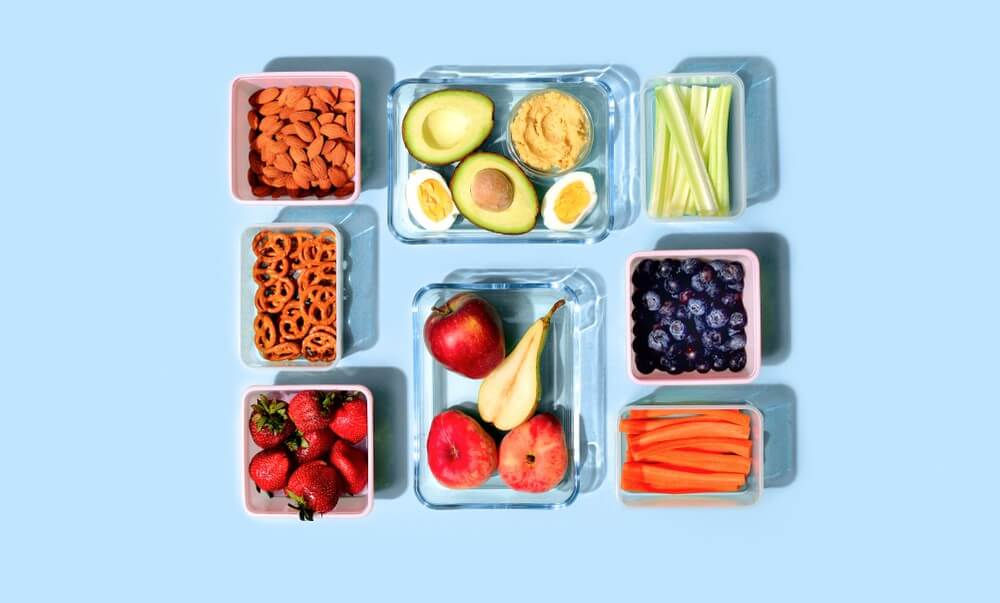

Eating windows are opportunities to nourish your brain and body efficiently with foods that energize and satisfy you. Here’s how to make those periods count no matter what fasting schedule you choose.
Basic Guidance for Any Eating Window
Whether you fast for 16 or 24 hours, keep these key principles in mind:
- Break Your Fast Mindfully: Choose easily digestible, nutritious foods like fruits, vegetables, or a protein-rich meal.
- Stay Hydrated: Continue drinking water (plain, sparkling, or mineral) during eating windows.
- Listen to Your Body: Eat until satisfied, not overly full. If you feel unwell, it’s okay to end your fast early.
What breaks a fast? Maintain the benefits of a true fast by avoiding:
- Cream or milk in beverages
- Flavored or sweetened drinks
- Supplements that contain calories
- Small bites or tastes of food
- Sweeteners (even zero-calorie options)
Staying hydrated is an excellent way to support your fast and your overall health. Water is an ideal choice, but other beverages are permitted during fasting, too.
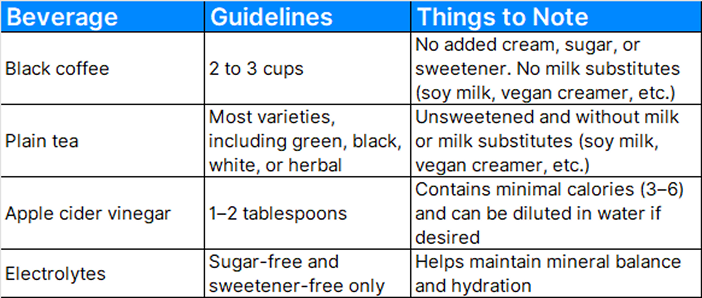
Remember, your fasting window is about giving your body time to activate beneficial repair processes. Keep it simple with water and unsweetened drinks — and don’t be afraid to recalibrate if your current schedule feels unsustainable.
Choosing nutritious foods during eating windows will amplify the benefits of intermittent fasting, rounding out a diet that truly nourishes your body and brain. Include brain-boosting foods like:
- Fatty fish rich in omega-3s
- Colorful fruits and vegetables
- Nuts and seeds
- High-quality proteins
- Whole grains
- Healthy fats like olive oil and avocados
Eating Window Strategies
Whether you’re putting together a 16/8 intermittent fasting 7-day meal plan or opting for the OMAD method, each fasting pattern offers unique ways to organize your meals.
16/8 or 18/6 Schedule
- Two to three well-balanced meals
- Ample hydration throughout the day
- Example window (16/8): 12 PM to 8 PM
- Midday meal around 12 to 1 PM
- Light snack if needed
- Evening meal between 5 and 7:30 PM
- Example window (18/6): 12 PM to 6 PM
- Midday meal around 12 to 1 PM
- Light snack if needed
- Evening meal between 4 and 5:30 PM
20/4 or OMAD
- Focus on a substantial, well-balanced meal.
- Include a variety of nutrients in a single meal.
- Take time to eat slowly (aim for 30-45 minutes).
- Stay hydrated before and during your meal.
- Include:
- Quality protein (fish, lean meats, eggs, legumes)
- Healthy fats (avocado, olive oil, nuts and seeds)
- Various colorful vegetables for nutrients
- Complex carbohydrates for sustained energy
- Fiber-rich foods to help you feel satisfied longer
- Avoid rushing or overeating just because the window is short.
Modified Fasting (5:2 or Alternate-Day Approach)
- Regular eating days: Enjoy normal, balanced meals.
- Modified fasting days: Consider skipping a meal or snack, and opt for low-calorie foods; choose foods high in protein and fiber to help with satiety.
With the right approach, modified fasting still allows for dedicated meal times each day.
Use the following two- or three-meal approaches for guidance.
Two-Meal Approach (600 calories total)
- Mid-morning (280 cal)
- 2 scrambled eggs with spinach (180 cal)
- 1 cup mixed berries (65 cal)
- Black coffee or tea (0 cal)
- Small apple (35 cal)
- Early evening (320 cal)
- Large mixed green salad with:
- 4 oz grilled chicken breast (160 cal)
- 1 tbsp olive oil vinaigrette (90 cal)
- Unlimited leafy greens (~10 cal)
- 1/4 avocado (60 cal)
- Large mixed green salad with:
Three-Meal Approach (~150 calories each)
- Breakfast (140 cal)
- Greek yogurt (0% fat, 100 cal)
- 1/2 cup blueberries (40 cal)
- Green tea (0 cal)
- Lunch (120 cal)
- Tuna lettuce wrap with:
- 2 oz tuna in water (60 cal)
- 2 romaine lettuce leaves (10 cal)
- 1 tbsp light mayo or mustard (15 cal)
- 2 tbsp diced celery (10 cal)
- Sliced cherry tomatoes (15 cal)
- Cucumber slices (10 cal)
- Tuna lettuce wrap with:
- Dinner (130 cal)
- 3 oz grilled whitefish (100 cal)
- Steamed broccoli (30 cal)
- Lemon and herbs (minimal calories)
Guidance for Intermittent Fasting by Age
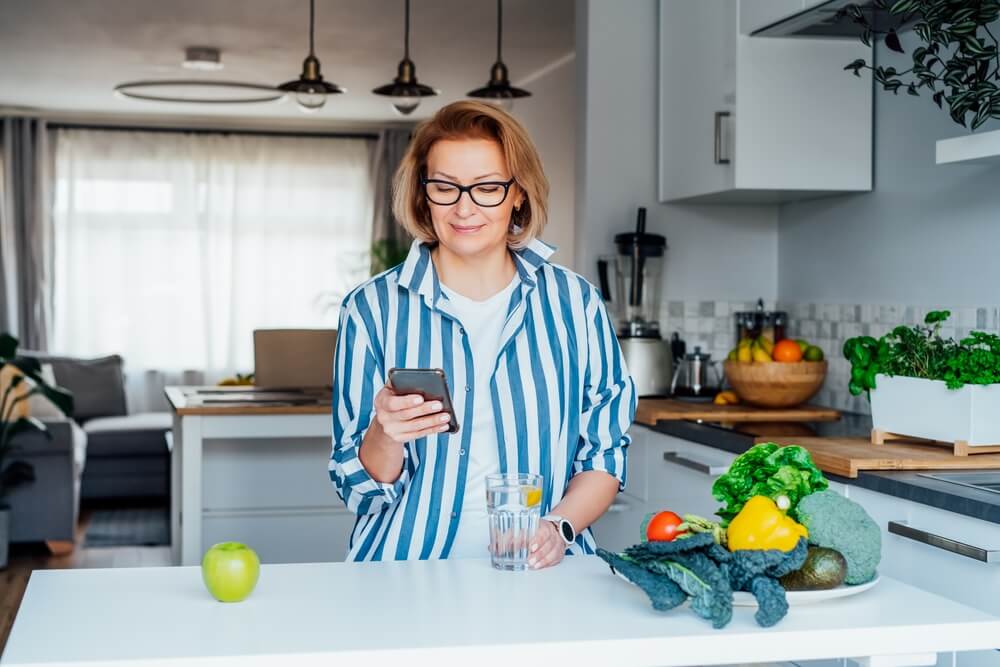

Just as your body’s needs change over time, your approach to intermittent fasting can evolve with age. Consider these age-related guidelines.
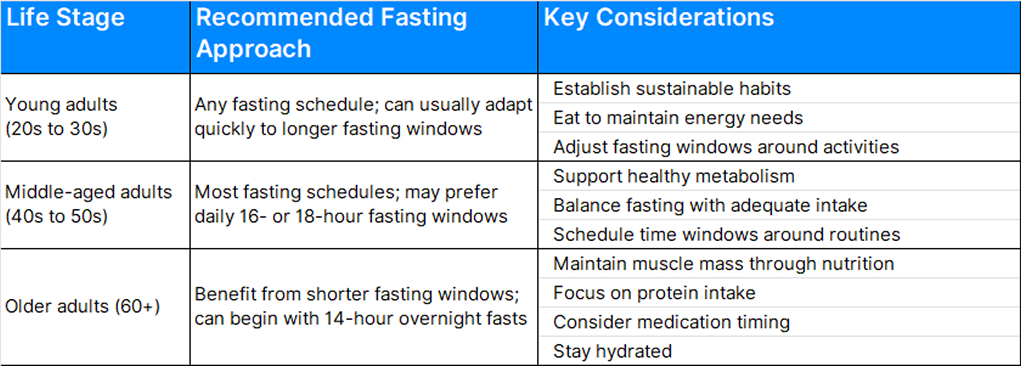
As you age, consider these factors when adjusting your fasting practice:
- Energy Needs: Your metabolism and energy requirements may change, often decreasing with age.
- Daily Schedule: Choose fasting windows that align with your routine.
- Activity Level: Adjust fasting periods around physical activity.
- Medications: Work with your healthcare provider to time medications appropriately.
Keep in mind that these are general guidelines. Your personal health status, lifestyle, and goals matter more than age alone when determining your ideal fasting approach. If you have health conditions or take medications, check with your healthcare provider before starting intermittent fasting.
Explore More About Fasting, Nutrition, and Brain Health
Your intermittent fasting journey starts with understanding your body’s natural rhythms and choosing an approach accordingly. The above intermittent fasting charts offer a solid starting point for exploring methods to support brain health.
Learn more about the impact of nutrition on brain health with Aviv Clinics’ resources on healthy aging and the science of cognitive vitality.
Aviv Medical Program provides you with a unique opportunity to invest in your health while you age.


